Is your Android device feeling more like a digital jungle than a helpful tool? Are you overwhelmed by a chaotic mess of apps, some familiar, others mysteriously lurking in the background, draining your battery and consuming precious storage space? This guide, “Taming Your App Jungle: A Guide to Disabling and Managing Apps on Android,” offers practical solutions to regain control. Learn how to effectively disable and manage apps, reclaim valuable resources, and optimize your Android experience. We will cover everything from identifying resource-hogging apps to disabling bloatware and utilizing built-in Android app management tools. Take charge of your device and navigate your app jungle with confidence.
Whether you’re dealing with pre-installed apps you never use, or downloaded apps that have outlived their usefulness, understanding how to manage apps is essential for a smooth and efficient Android experience. This comprehensive guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions for disabling apps, uninstalling apps, and effectively using Android’s app management features. Learn how to identify bloatware and reclaim valuable system resources. Taming your app jungle isn’t just about freeing up space; it’s about optimizing performance and creating a personalized digital environment tailored to your needs.
Why Disable Apps? Benefits for Performance and Battery Life
Disabling unused apps can significantly improve your Android device’s performance and extend its battery life. Many apps, even when not actively used, continue to run background processes and services. These processes consume valuable system resources, such as processing power (CPU) and random access memory (RAM).
By disabling these apps, you effectively free up these resources. This can lead to a noticeable boost in overall system speed, smoother multitasking, and a more responsive user experience. Reduced CPU load translates to less strain on your device’s processor, preventing overheating and improving performance consistency.
Furthermore, background processes often consume battery power. Disabling unused apps can minimize battery drain, allowing your device to last longer on a single charge. This is especially beneficial for apps that frequently sync data or maintain constant network connections.
Identifying Bloatware and Unnecessary Apps
Recognizing bloatware and unnecessary apps is the first step towards a cleaner, more efficient Android experience. Bloatware typically refers to pre-installed applications that come with your device from the manufacturer or carrier. These apps often cannot be fully uninstalled without rooting your device, but they can usually be disabled.
Unnecessary apps, on the other hand, are apps you installed yourself but no longer use. They might be games you’ve finished, utility apps that are no longer relevant, or social media platforms you’ve abandoned.
To identify these apps, start by reviewing your app drawer. Look for apps you don’t recognize or remember installing. Consider how frequently you use each app. If you haven’t used an app in months, it’s likely a candidate for disabling or uninstalling. Pay particular attention to apps that run in the background, as these can consume resources and drain battery life even when not actively in use. You can check background app usage in your device’s settings.
Key indicators of bloatware include apps with generic names, duplicated functionalities with other apps, and apps that constantly push notifications you don’t find useful.
Disabling Apps Through System Settings
Disabling apps through your Android system settings is a straightforward process that offers a balanced approach between uninstalling and leaving apps untouched. It effectively neutralizes an app’s impact on system resources without completely removing it.
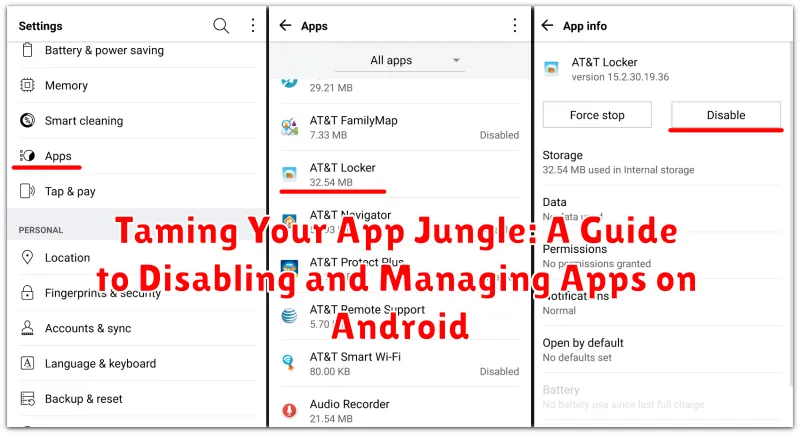
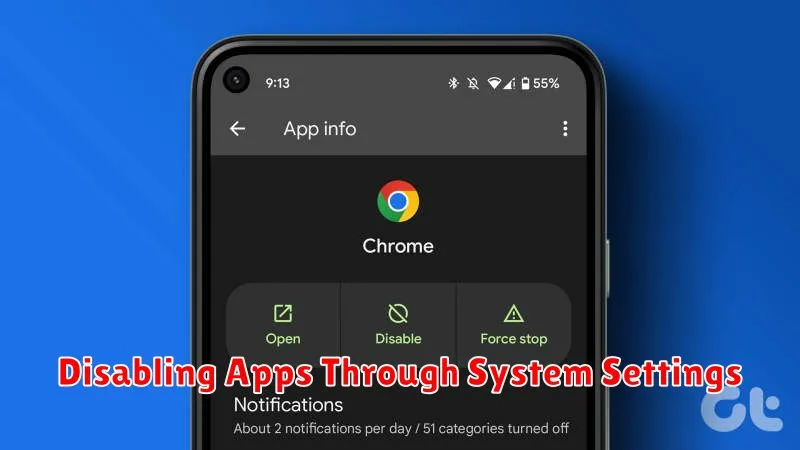
To disable an app, navigate to your device’s Settings. The exact path may vary slightly based on your Android version and manufacturer, but it generally involves accessing the Apps or Applications section. Here, you’ll find a list of all installed applications.
Select the app you wish to disable. On the app’s info screen, you should see a Disable button. Tapping this button will prevent the app from running in the background, sending notifications, and consuming system resources. Note that some pre-installed system apps might not offer the disable option.
Important Considerations: Disabling an app may affect other apps that rely on it. Pay attention to any warnings presented before confirming the disable action. If you experience any unexpected issues after disabling an app, you can easily re-enable it through the same process.
Using Third-Party Apps for Advanced App Management
While Android’s built-in settings offer basic app management, third-party apps provide more advanced features for controlling your app ecosystem. These apps can simplify batch disabling, offer detailed app usage statistics, and sometimes even provide root-level control for more granular management.
Several popular app management tools are available on the Google Play Store. Look for apps that offer features like batch disabling/enabling, app usage tracking, and permission management. These tools can be especially helpful for identifying resource-intensive apps and managing multiple apps simultaneously.
Important Note: Granting extensive permissions to third-party app management tools can pose a security risk. Always download reputable apps from trusted sources and carefully review the permissions they request before granting access.
Understanding the Difference Between Disabling and Uninstalling
Disabling and uninstalling apps might seem similar, but they have key differences impacting your Android device. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective app management.
Disabling an app essentially puts it in a dormant state. The app remains on your device, but it’s deactivated. Its icon is hidden, and it can’t run in the background or send notifications. System apps are often disabled this way to prevent them from consuming resources while remaining available for potential future use.
Uninstalling, on the other hand, completely removes the app and its associated data from your device. It frees up storage space and eliminates any potential impact on performance. Unlike disabled apps, uninstalled apps require re-downloading from the Google Play Store to be used again.
Consider disabling when you want to temporarily stop an app without deleting it completely. Choose uninstalling when you no longer need an app and want to reclaim storage.
Re-Enabling Apps When Needed
Disabling apps is a great way to declutter your device and save resources, but you might need those apps again sometime. Thankfully, re-enabling them is a straightforward process.
Accessing Disabled Apps: Navigate to your device’s Settings. The exact path may vary slightly depending on your Android version and manufacturer, but generally, you’ll look for an “Apps” or “Applications” section. Within this section, you might need to select “See all apps” or a similar option to view a comprehensive list.
Enabling an App: From the list of apps, locate the disabled app you want to re-enable. Tap on the app’s name, and you should see an “Enable” button. Tap this button to restore the app’s functionality. The app will then be available for use just as it was before you disabled it.
Restoring App Data: In some cases, disabling an app might clear its associated data. If you find that the app doesn’t retain its previous settings or information after re-enabling, you might need to manually reconfigure the app or restore data from a backup if one exists.
Managing App Permissions for Enhanced Privacy
Controlling app permissions is crucial for protecting your privacy on Android. Apps often request access to various features and data on your device, and managing these permissions allows you to limit what information they can access.
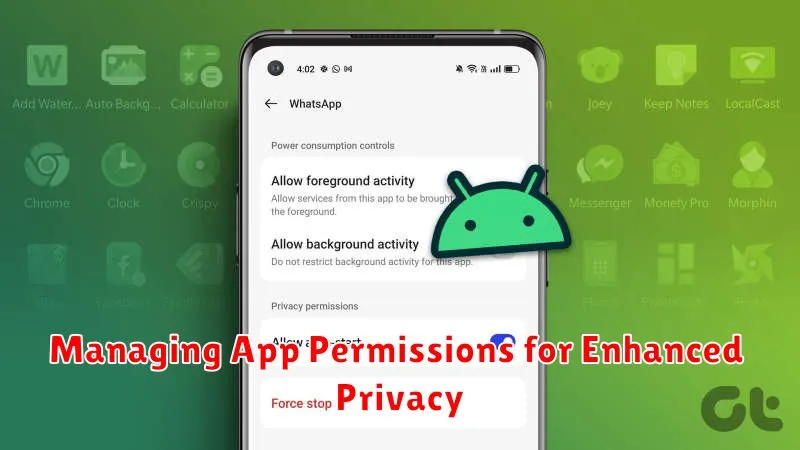
You can review and modify permissions for each app individually. Access the app settings through your device’s settings menu. Look for the “Apps” or “Applications” section, then select the specific app you want to manage. Within the app’s settings, you’ll find a “Permissions” section. This section lists all the permissions the app has requested or currently has access to, such as location, camera, microphone, contacts, and storage.
For each permission, you can typically choose to allow or deny access. Carefully consider the necessity of each permission in relation to the app’s functionality. If an app’s requested permission seems unnecessary or excessive, it’s best to deny it.
Regularly reviewing app permissions is a good practice. Android updates may introduce new permission categories, and apps themselves can update their permission requirements. Staying informed and actively managing these permissions helps you maintain better control over your privacy.
Tips for Optimizing App Performance
Regularly update your apps. Developers frequently release updates that include performance enhancements, bug fixes, and optimizations. Keeping your apps up-to-date ensures you’re leveraging the latest improvements.
Clear app caches and data. Over time, apps accumulate cached data that can sometimes hinder performance. Clearing the cache can free up resources and improve responsiveness. Be mindful that clearing data will reset app settings and require you to log in again.
Limit background processes. Some apps consume resources even when not actively in use. Restricting background activity for less frequently used apps can improve overall system performance. Check your device’s settings for background process management options.
Use Lite versions of apps (when available). Many popular apps offer “lite” versions designed for lower-spec devices or users who prioritize data conservation. These versions often have a smaller footprint and consume fewer resources.
Restart your device periodically. A simple restart can resolve temporary performance issues by clearing memory and closing background processes.