When your electronic device starts acting up, a reset can often be the solution. But with terms like factory reset and hard reset often used interchangeably, it can be confusing to know which method is appropriate for your situation. Understanding the differences between a factory reset and a hard reset is crucial for troubleshooting effectively and ensuring you choose the right approach to resolve your device’s issues. This article will clarify the distinctions between these two reset methods, highlighting when to use a factory reset versus a hard reset. We’ll explore the implications of each process, helping you make an informed decision when facing device malfunctions or simply seeking a fresh start.
Whether you’re dealing with a smartphone, tablet, computer, or another electronic device, knowing the nuances of factory reset vs. hard reset is essential. This article will delve into the specifics of each method, explaining what data is affected, how each reset is performed, and the circumstances under which each is recommended. By understanding these differences, you can confidently perform the necessary reset procedure to address performance problems, software glitches, or simply prepare your device for sale or transfer. Learn the differences between a factory reset and hard reset and equip yourself with the knowledge to troubleshoot your devices effectively.
What is a Factory Reset?
A factory reset, also known as a master reset, is a software-driven process that returns a device to its original configuration as it was when it left the factory. This process removes all user data, including installed apps, personal files, and customized settings. It essentially erases everything added to the device after purchase, restoring it to a clean slate.
Key Characteristics of a Factory Reset:
- Software-based: Initiated through the device’s settings menu.
- Complete data erasure: Removes all user-added data and settings.
- Restores factory defaults: Returns the device to its out-of-the-box state.
- Typically used for: Troubleshooting software issues, preparing a device for sale, or general performance improvement.
A factory reset is a non-destructive process to the device’s hardware and operating system files. It simply removes the user’s personalized layer on top of the existing system.
What is a Hard Reset?
A hard reset, also known as a cold boot or force restart, is a more abrupt method of restarting a device than a factory reset. It involves cutting off power to the device and then restarting it. This process doesn’t erase any data (except for volatile RAM) and is primarily used to resolve temporary software glitches or when a device becomes unresponsive.
Think of it like rebooting your computer when it freezes. A hard reset forces the device to shut down and restart without going through the usual shutdown process. It clears the device’s memory and restarts the operating system afresh.
There are various ways to perform a hard reset, depending on the device. This can range from simply holding down the power button for an extended period, to using a specific key combination, or even removing the battery (if possible).
Key Differences Between Factory Reset and Hard Reset
While both factory and hard resets restore a device to its original state, they differ in how they achieve this and what they affect.
A factory reset is a software-driven process, initiated through the device’s settings. It erases user data and settings, returning the device to its factory default configuration. It usually retains the operating system.
A hard reset, also known as a hardware reset, is typically performed using button combinations or by interrupting the power supply. It often involves a lower-level reset, which might clear cached data and settings beyond the scope of a factory reset. Some hard resets might even reload firmware.
| Feature | Factory Reset | Hard Reset |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Software (Settings menu) | Hardware (Button combination, power interruption) |
| Data Affected | User data, settings | User data, settings, cached data (potentially firmware) |
| Operating System | Usually retained | May be reinstalled (depending on the method) |
When to Perform a Factory Reset

A factory reset is a useful tool in various situations where software issues plague your device. Consider a factory reset when you experience persistent software problems, like frequent app crashes, unexplained slowdowns, or unusual operating system behavior that troubleshooting hasn’t resolved.
Preparing to sell or give away your device necessitates a factory reset to remove all personal data and restore the device to its original out-of-box state. This protects your privacy and ensures the new owner receives a clean slate.
If you’ve forgotten your device’s passcode or PIN and have exhausted other recovery options, a factory reset can offer a way to regain access, though it will result in data loss. Similarly, if your device is infected with malware or experiencing severe software conflicts, a factory reset can often serve as an effective solution.
Finally, if you are experiencing minor software glitches or simply want to improve your device’s performance, a factory reset can provide a fresh start and potentially alleviate these issues.
When to Perform a Hard Reset
A hard reset is a more drastic measure than a factory reset and should be reserved for specific situations where a factory reset isn’t feasible or hasn’t resolved the issue. Consider a hard reset when encountering the following:
Device Unresponsiveness
If your device becomes completely unresponsive, frozen, or stuck in a boot loop and you cannot access the settings menu to perform a factory reset, a hard reset may be the only option to regain control.
Software Glitches or Errors
Sometimes, software glitches or corrupted files can cause significant problems that a factory reset cannot address. In such cases, a hard reset may be necessary to restore the device to a functional state.
Forgotten Passcode or Pattern
If you have forgotten your device’s passcode, PIN, or pattern, and have exhausted other recovery options, a hard reset may be necessary to regain access. Keep in mind this will erase all data on the device.
Pre-Sale Preparation (With Caution)
While a factory reset is generally sufficient for preparing a device for sale, a hard reset can offer an extra layer of data removal for enhanced security. However, exercise caution as improper execution can damage the device.
How to Perform a Factory Reset on Android
A factory reset restores your Android device to its original factory settings, erasing all user data. It’s typically done through the device’s settings menu, though the exact steps may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and Android version. Back up important data before proceeding, as this process is irreversible.
Steps for a Typical Factory Reset:
- Open the Settings app on your device.
- Navigate to System (or similar, such as “General Management”).
- Look for Reset options (may be labeled “Reset options,” “Backup & reset,” or similar).
- Select Factory data reset.
- The system will warn you about data loss. Confirm your choice by tapping Reset Phone or an equivalent option.
- Your device will restart and perform the factory reset. This process may take several minutes.
- Once complete, your device will boot up as if it were new.
How to Perform a Hard Reset on Android
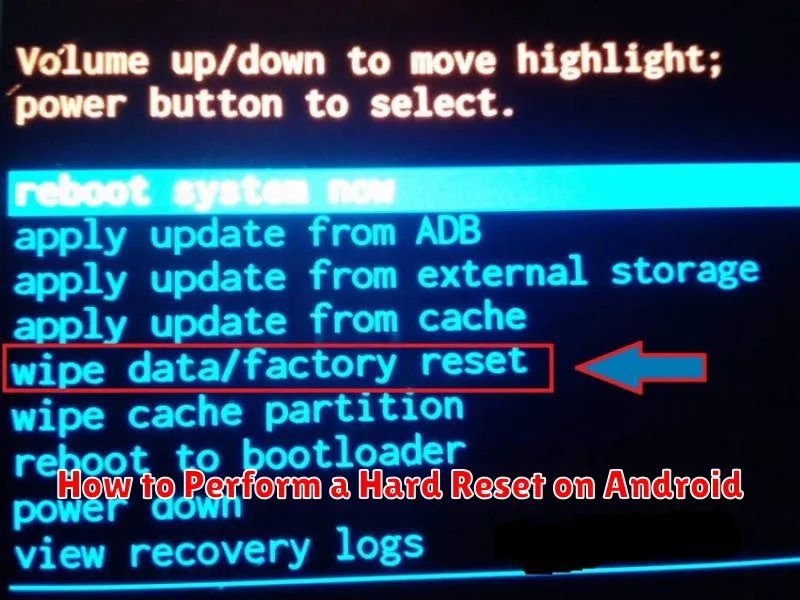
A hard reset, also known as a hardware reset or recovery mode reset, bypasses the Android operating system and resets the device to its factory default settings using hardware buttons. This method is usually employed when the device is unresponsive or cannot boot normally.
The process varies slightly between different Android devices, but the general steps are similar. Power off your device completely. Then, press and hold a specific combination of buttons to enter recovery mode. This combination is typically Volume Down + Power, Volume Up + Power, or Home + Volume Up + Power, but it could differ depending on your device’s manufacturer and model. Consult your device’s manual for the precise combination.
Once in recovery mode, you’ll navigate using the volume buttons and select options using the power button. Use the volume buttons to highlight “Wipe data/factory reset” and press the power button to select it. Confirm your choice by selecting “Yes” on the following screen. After the reset process completes, select “Reboot system now“.
It is crucial to understand that a hard reset will erase all data on your device. Backup any important data before proceeding.
Precautions Before Performing a Reset
Before initiating either a factory reset or a hard reset, taking certain precautions is crucial to prevent data loss and ensure a smooth process.
Back Up Your Data
The most important precaution is to back up all important data. This includes photos, videos, documents, contacts, and app data. Both factory and hard resets will erase data on the device’s internal storage.
Charge Your Device
Ensure your device has sufficient battery charge. A reset process interrupted by a power failure can lead to software issues and potential data corruption. Ideally, have your device plugged into a power source during the reset.
Remove Your Accounts
For security, it’s recommended to remove your Google account (and any other associated accounts) from the device before performing a reset. This can help avoid potential complications with Factory Reset Protection (FRP) after the reset.
Know Your Passwords
After the reset, you’ll need your Google account credentials (and any other account passwords) to set up the device again. Ensure you remember these passwords or have them securely stored elsewhere.

